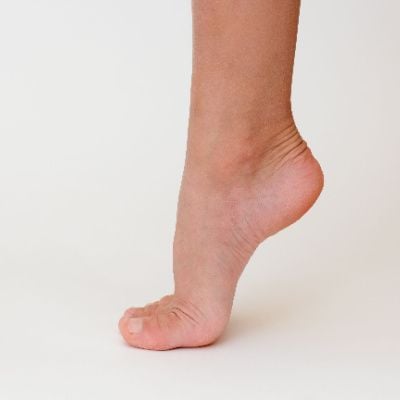
 Cavus foot, commonly referred to as a high-arched foot, is a structural anomaly that can impact the biomechanics of the lower extremities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of cavus foot, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective management strategies. By shedding light on this often overlooked condition, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge to recognize, address, and seek appropriate care for cavus foot.
Cavus foot, commonly referred to as a high-arched foot, is a structural anomaly that can impact the biomechanics of the lower extremities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of cavus foot, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective management strategies. By shedding light on this often overlooked condition, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge to recognize, address, and seek appropriate care for cavus foot.
Unraveling Cavus Foot - What Is It?
Defining Cavus Foot
Cavus foot is characterized by an unusually high arch in the midfoot region. Unlike the more common flat feet, cavus foot presents challenges related to weight distribution and shock absorption.
Anatomy of the High-Arched Foot
Understanding the anatomy of the foot is essential in grasping the nuances of cavus foot. Ligaments, tendons, and bones work together to maintain the arch structure, and any imbalance can result in a high-arched foot.
Causes and Risk Factors
Neurological Conditions
Neurological disorders, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, can lead to muscle imbalances in the foot, contributing to the development of cavus foot. Nerve damage disrupts the normal functioning of foot muscles.
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders affecting muscle function, may manifest as cavus foot due to muscle weakness and imbalances. Recognizing the connection between these conditions is pivotal in addressing foot abnormalities.
Trauma or Injury
Injuries to the foot, particularly fractures or damage to the ligaments, can result in a high-arched foot. Trauma-induced cavus foot requires careful assessment and appropriate intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms of Cavus Foot
Foot Pain
Individuals with cavus foot may experience pain, particularly in the arch and heel regions. The high arch can lead to increased pressure on specific areas of the foot, contributing to discomfort.
Instability and Frequent Ankle Sprains
The elevated arch of cavus foot can reduce the foot's surface area in contact with the ground, leading to instability. This instability increases the risk of ankle sprains, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures.
Calluses and Corns
Uneven weight distribution on the foot may result in the formation of calluses or corns in response to increased pressure. Identifying these signs is crucial in addressing foot health.
Diagnosing Cavus Foot
Clinical Examination
Healthcare professionals conduct a comprehensive clinical examination, assessing the patient's medical history, symptoms, and conducting a physical examination of the foot. An understanding of the individual's gait is essential.
Imaging Studies
X-rays and other imaging studies may be ordered to visualize the bones and joints of the foot. These images help in assessing the severity of the high arch and identifying any associated abnormalities.
Electromyography (EMG)
In cases where neurological conditions are suspected, electromyography may be performed to assess nerve function and muscle activity. This test provides valuable insights into the underlying cause of cavus foot.
Treatment Strategies for Cavus Foot
Orthotic Devices
Custom orthotic devices play a crucial role in managing cavus foot. These inserts are designed to provide support, distribute pressure evenly, and promote proper foot alignment.
Supportive Footwear
Choosing footwear with proper arch support and cushioning is essential for individuals with cavus foot. Shoes that accommodate the high arch help mitigate discomfort and prevent complications.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy aims to strengthen weakened muscles and improve flexibility. Targeted exercises address muscle imbalances, enhancing overall foot function.
Surgical Interventions
Tendon Transfer
In cases where muscle imbalances contribute to cavus foot, tendon transfer surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves repositioning tendons to achieve a more balanced foot structure.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy, a surgical procedure involving the reshaping of bones, may be considered to address structural abnormalities contributing to the high arch. Surgical interventions are tailored to the individual's specific needs.
Preventive Measures for Cavus Foot
Regular Foot Checks
Regular self-examinations of the feet allow individuals to monitor any changes or discomfort associated with cavus foot. Early detection facilitates timely intervention.
Proper Footwear from Childhood
Encouraging proper footwear choices from childhood can prevent the progression of cavus foot. Well-fitted shoes with adequate arch support are crucial for healthy foot development.
Gait Analysis
Conducting gait analysis can identify abnormal walking patterns early on. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention and management of cavus foot.
Living with Cavus Foot
Daily Foot Care
Maintaining good foot hygiene and addressing any calluses or corns promptly is essential for individuals with cavus foot. Regular moisturization and proper trimming of nails contribute to overall foot health.
Physical Activity Modifications
Engaging in low-impact exercises and modifying physical activities can help individuals with cavus foot manage their condition. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals ensures safe and enjoyable physical activity.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Podiatrists and Orthopedic Specialists
Consulting with podiatrists or orthopedic specialists ensures a comprehensive assessment of cavus foot. These professionals provide tailored recommendations based on the individual's unique condition.
Neurologists
For cases associated with neurological conditions, collaboration with neurologists is crucial. Addressing the underlying neurological cause contributes to effective management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cavus foot is a condition that necessitates understanding and proactive management. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and available treatment strategies, individuals can navigate the complexities of cavus foot with informed decision-making. Whether through conservative measures such as orthotic devices and physical therapy or surgical interventions tailored to the specific needs of the individual, a comprehensive approach ensures the best outcomes for high-arched foot health. Through a combination of preventive measures, timely intervention, and collaborative care with healthcare professionals, individuals can embark on a journey towards alleviating cavus foot and fostering overall foot well-being.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for educational and information purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a licensed medical provider and follow their recommendations regardless of what you read on this website. If you think you are having a medical emergency, dial 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Links to other third-party websites are provided for your convenience only. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms of use for those websites. Neither Lyle Modlin, nor any contributor to this website, makes any representation, express or implied, regarding the information provided on this website or any information you may access on a third-party website using a link. Use of this website does not establish a doctor-patient relationship. If you would like to request an appointment with a health care provider, please call our office at (410) 263-3100.